Automotive Steel Processing: AHSS and Galvanized Steel

Steel continues to be the frontrunner when it comes to car manufacturing because of its strong and dependable nature. According to worldsteel.org, there are several benefits of using steel in automotive production. Steel:
● Contains recycled steel and is endlessly recyclable.
● Has lower CO2 life cycle emissions than any other automotive material.
● Enables engineering of crash-resistant structures.
● Is a higher strength steel that enables lightweight vehicle construction that is stronger, safer, and more fuel-efficient
● Enables creative, flexible designs.
● Is easy to repair with existing techniques and equipment, making repairs more affordable.
● Is cost efficient compared to all other structural materials.
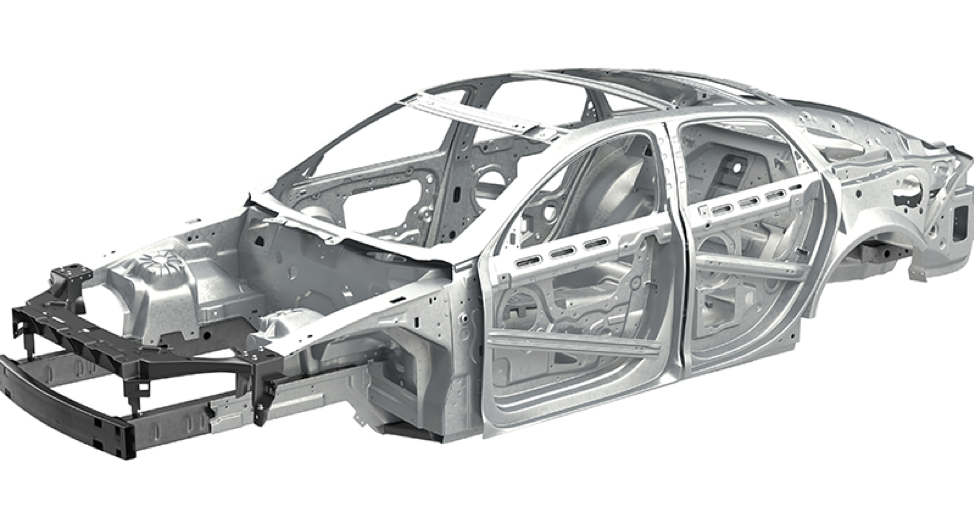
There are several common uses for steel in an automotive vehicle. Most of this steel is found in the skeletal body of the vehicle, often called the “body in white,” which is the foundation from which the rest of the vehicle is created.
Bumpers and Reinforcements
Bumpers are some of a vehicle’s first defenses against any major impact, thus they demand a very high level of force absorption. The durability and crash resistance of high strength steels make it a great option for bumper systems. Further driving its use is the ability to employ a thinner steel, promoting additional weight savings. UHSS bumpers are typically roll formed. For more detailed information on steel bumper systems for passenger cars and light trucks, visit this website: https://www.a-sp.org/-/media/doc/smdisteel/bumpers/smdi-steel-bumper-systems-manual-6th-edition—january-2019—final.ashx
There are many other areas of a car that need strong reinforcement. Sill reinforcements and cross-members, for instance, both require high energy absorption. Stiffness can be maintained when transitioning to thinner panels by changing the geometry of the parts. High strength steels are well suited for these forming challenges, with the reduced thickness leading to a lighter weight part.
Door Beams and Seating
Again, weight savings are a major consideration here. Side impact beams are now commonly made using the highest strength steels, leading to both increased safety and lighter weight products. While seats are not traditionally considered part of the Body-in-White, they are some of the heaviest items in a passenger vehicle. As such, they are prime candidates for lightweighting using high strength and durable steels.
Chassis and Frames
High-strength steel benefits the entire frame’s support capabilities. The chassis is subject to some of the most extreme stresses seen on any of a car’s parts, so it needs excellent fatigue resistance properties – such as those found in high-quality steel. Using high strength, high formability steels allows the vehicle designer the flexibility to create lightweight complex shapes while maintaining the structural integrity demanded by the application.

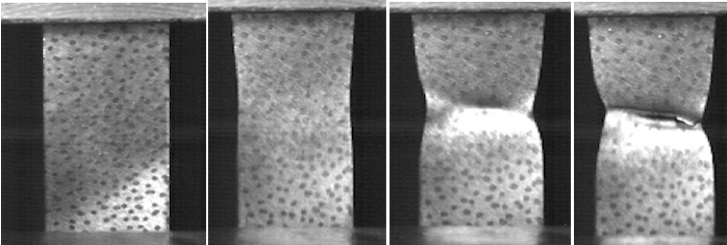
Advanced High Strength Steel
Forbes.com recently cited that […]