WHAT ARE TRIP STEELS (Transformation Induced Plasticity Steels)?
TRIP Steels (Transformation Induced Plasticity Steel) are part of the Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS) family.
The microstructure of TRIP steels consists of at least five-volume percent of retained austenite, which is embedded in a primary ferrite matrix. The microstructure also contains hard phases like bainite and martensite in varying amounts.
TRIP steels are notable due to the higher carbon content than other members of the AHSS family, such as dual phase steels. They typically require the use of an isothermal hold at an intermediate temperature, which produces some bainite. Silicon and aluminum are added in order to both accelerate the ferrite and bainite formation process, as well as avoiding carbide buildup in the bainite region of the material.
Greater silicon, aluminum, and carbon content of TRIP steels result in large fractions of retained austenite in the material’s final microstructure. The increased carbon content also stabilizes the retained austenite phase below the usual ambient temperature.
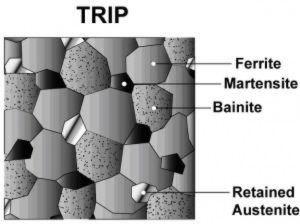
Changing the carbon content helps to control the strain level at which the austenite begins to transform into martensite. At low carbon levels, the transformation of the retained austenite will begin almost immediately upon deformation, which will then improve the formability and work hardening rate during the stamping process.
At higher carbon content, the transformation will occur only at strain levels beyond those utilized during the forming processing. The retained austenite remains after the final stage of the forming process at these higher carbon levels – the transformation into martensite will occur only during subsequent deformation; in the case of automobiles, an example would be a crash event.
PROPERTIES OF TRIP STEELS
TRIP Steels can be produced as hot-rolled, cold-rolled, or hot dip galvanized, with a strength range from 500 MPa to 800 MPa.
TRIP Steels are highly sought after due to their high work hardening rate, which is created by the hard second phases that are dispersed in the soft ferrite during deformation. Despite the fact that initial work hardening rate of the material is lesser than that of, say, dual phase steels, TRIP steels sustain their hardening rate at much higher strain levels, where DP steel’s work hardening rate would deteriorate.
As a result of the high work hardening rates, TRIP steels also have substantial stretch forming properties.
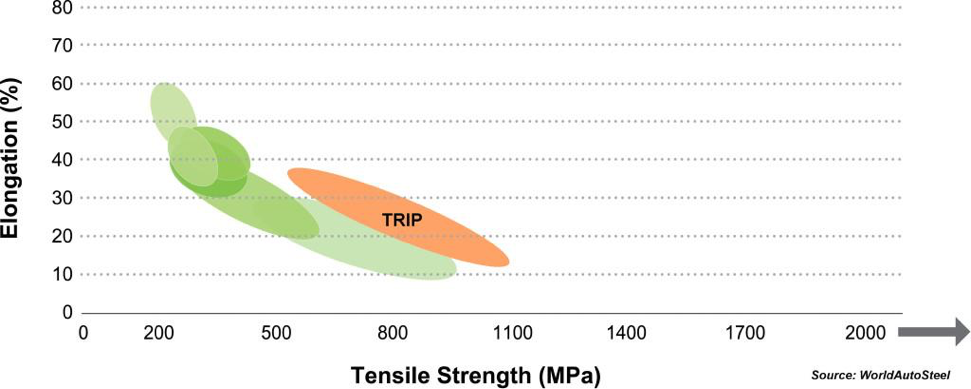
The high strain hardening capacity and mechanical strength make these steels an excellent candidate for automotive parts that require a high energy absorption capacity. TRIP steels also have a strong bake hardening following deformation, which even further improves their crash performance.
To summarize TRIP steel’s properties:
- Work hardening – When compared to other advanced high-strength steels, TRIP steels exhibit and retain a higher work hardening rate at higher levels of strain.
- Formability – As a byproduct of the high work hardening rate, these steels have substantial stretch forming properties, and can be put through stamping processes in a relatively stable manner.
- Bake hardening – TRIP steels have a very high bake hardening capacity, and can by doing so can increase their yield strength by close to 70 MPa.
- Product mass reduction capacity – Due to the above characteristics, these steels are good candidates for weight reduction and part down gauging techniques.
APPLICATION OF TRIP STEELS IN AUTOMOBILES
TRIP steels are excellent for automotive parts that require high work hardening during crash deformation and large amounts of energy absorption.
They are also very well-suited for creatingcomplicated, hard-to-form parts, which is a result of their high formability and work hardening attributes. Thus, they are handy for complex reinforcement and structural parts.
Current production grades of TRIP steels and example automotive applications:
TRIP 350/600 Frame rails, rail reinforcements
TRIP 400/700 Side rail, crash box
TRIP 450/800 Dash panel, roof rails
TRIP 600/980 B-pillar upper, roof rail, engine cradle, front and rear rails, seat frame
TRIP 750/980
About National Material L.P. – National Material Limited Partnership and its affiliates have a long history of quality and service dating back to 1964. Since its founding, National Material L.P. has grown to over 30 business units and is now one of the largest suppliers of steel in America. The National Material group of industrial businesses consists of the Steel Group, Stainless and Alloys Group, Raw Material Trading Group, Aluminum Group, and Related Operations.
Visit National Material: https://www.nationalmaterial.com or call (U.S.) 847-806-7200.





