 WHAT IS STEEL PICKLING?
WHAT IS STEEL PICKLING?
Steel pickling refers to a treatment that is used to remove impurities, rust, and scale from the surface of a material. During hot working processes, an oxide layer (referred to as “scale”, due to the scaly nature of its appearance) develops on the surface of the metal. Before most cold rolling processes, previously hot rolled steel goes through a pickling line to remove the scale from the surface and make it easier to work. To restore the best corrosion resistant performance, the damaged metal layer must be removed, exposing a fully alloyed stainless steel surface.
In order to remove this oxide layer, the material is dipped into a vat of what is called “pickle liquor”. Pickle liquor can come in many forms; carbon steels with an alloy content of less than 6% are often pickled in hydrochloric or sulfuric acid. For steels that have a higher carbon content, a two-step pickling process is required, with additional acids used (phosphoric, hydrofluoric, and nitric acid).
Steel processing companies that offer hot and cold rolling services typically encounter two different types of scale – high-temperature and low-temperature scale. High temperature milling processes create three layers of iron oxide, which forms on the material after at temperatures above 1070F. Low temperature mill scale develops in procedures that use temperatures below 1070.
TYPES OF ACID USED IN STEEL PICKLING:
Hydrochloric
Advantages:
- Reduce heating costs since pickling solutions are used at room temperature
- More extensive scale removal
- Less penetration of hydrogen by diffusion
- Less deposition of iron salts on the pickled surface
Disadvantages:
- Fumes when heated above ambient temperatures
- Acid recovery systems are expensive
- More corrosive toward equipment
- Magnesium Higher disposal costs than sulfuric acid
Sulfuric
Advantages:
- Acid can be renewed more frequently
- Raising temperature will allow lower acid concentrations to pickle effectively
- Ease of recovering iron sulfate
- The rate of pickling can be controlled by varying the temperature
Disadvantages:
- Greater acid attack on base metal.
- Greater hydrogen diffusion into the steel
- Pickling residues are more adherent
- Acid solutions must be heated
After the steel pickling process, sheet steel will typically oxidize after long exposure to atmospheric conditions that experience high humidity. To counteract this, a film of oil or other waterproof coatings are applied to create a shield of moisture in the air.
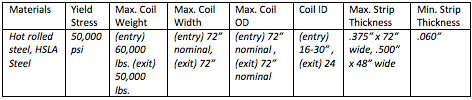
National Material’s Steel Pickling Capabilities:
About National Material L.P. – National Material Limited Partnership and its affiliates have a long history of quality and service dating back to 1964. Since its founding, National Material L.P. has grown to over 30 business units and is now one of the largest suppliers of steel in America. The National Material group of industrial businesses consists of the Steel Group, Stainless and Alloys Group, Raw Material Trading Group, Aluminum Group, and Related Operations.
Visit National Material: https://www.nationalmaterial.com or call (U.S.) 847-806-7200





