
No one has ever walked into a car dealership and said to the salesperson: “Hey, do you have anything made out of an unstable material?” When assembling vehicles, car manufacturers face a specific challenge: they need materials with seemingly contradictory properties: lightweight, but strong, and highly formable into rigid structures. This is a challenge in light of how metals deform. The strains from forming accumulate into localized areas on the part, leading to excessive thinning known as “necking.” These areas are thinner than the rest of the part, and are the most likely to have durability or fatigue problems during the vehicle life. Higher strength materials are more likely to experience “necking” during the production process, which, in turn, creates an unstable part. Most would agree that would never be a good quality in a car.
The first antidote to this challenge was introduced in the 1980’s when the steel industry developed interstitial free (IF) steels. These steels have a microstructure primarily consisting of a single phase known as ferrite, which is iron with typically less than 50ppm carbon in an interstitial solid solution. It has a body-centered cubic (bcc) structure at room temperature. ULC steels are highly formable, a desirable trait for auto companies that have a high demand for steel that can be molded into the new complex shape of cars. However, these steels are relatively soft which makes them poor candidates for the automotive body structures that need to withstand increasingly stringent crash resistance requirements. Steelmakers had to create new steel grades that combine mechanical strength with high ductility (the ability to undergo significant plastic deformation before rupture). Enter advanced high strength steel!
What is AHSS?

The metallurgy and processing of advanced high strength steel (AHSS) grades are somewhat novel compared to conventional steels. Their remarkable mechanical properties are the result of their unique processing and structure. They are classified into categories based on their microstructure or how they deform: dual phase (DP) steel, transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steel, complex phase (CP) steel, martensitic (MS) steel, ferritic bainitic (FB) steel, and twinning-induced plasticity (TWIP) steel. AHSS solves two distinct automotive needs by using two different groups of steels. The DP and TRIP grades of steel have increased values of the work hardening exponent. These possess higher strength levels with improved formability and crash-energy absorption compared to the current HSLA (High Strength, Low Alloy) grades. The CP and MS grades extend the availability of steel in strength ranges above the HSLA grades.
Additional steels are designed to meet specific process requirements. These include increased edge stretch flangeability, strengthening after forming, and improved bendability. By combining a number of different microstructures not traditionally found in conventional high strength steels and controlling the phase distribution, a wide range of properties are possible. This allows steel companies to tailor their processing to meet the ever-more focused application requirements demanded by the automotive industry.
Why is AHSS so beneficial for auto manufacturers?
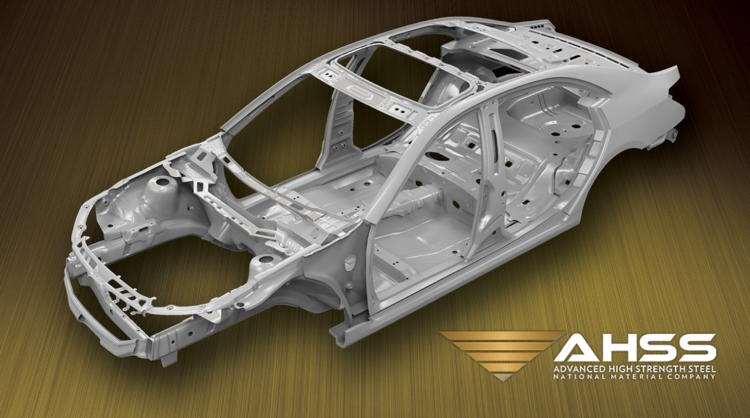

AHSS is most advantageous when used for safety components of automobiles and their structural parts where high strength with reasonable ductility is important. AHSS has become the material of choice for passenger safety cage components like sill reinforcements, A-pillars, B-pillars, side impact beams, waistline reinforcements, bumpers, and roof bows. Advanced high strength steel has also been introduced in all other vital areas of the automotive industry, like seats. Many new cars are already composed of 30% – 40% AHSS. The high strength of AHSS is a useful tool to reduce the weight of bumper systems, door side impact beams, seat structures, etc. The advantages of using AHSS are evident in all types of automobiles. Small cars benefit from greatly improved crash safety while heavier cars, like SUVs, can be made much more fuel efficient. There has been a smooth and cost-efficient transition from mild steels, or conventional high strength steels. The qualities of AHSS make it a leading success factor behind improvements the automotive industry.
AHSS in 2020: towards a clean future
Advanced high strength steel is beneficial for several reasons including:
- A decreased carbon-footprint. AHSS is strong, light, and produced with a reduced life cycle impact – helping automakers decrease a vehicle’s life-long carbon footprint.
- Fewer emissions The use of AHSS contributes to a 5% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. New grades of advanced high strength steels enable carmakers to reduce vehicle weight by 25-39% compared to conventional steel. When applied to a typical five-passenger family car, the overall weight of the vehicle is reduced by 170 to 270 kg, which corresponds to a lifetime saving of 3 to 4.5 tons of greenhouse gases over the vehicle’s total life cycle.
- Electric vehicles Like most automotive manufacturers, the producers of electrical vehicles favor AHSS over aluminum because it’s strong and cost effective. Electric vehicles are gaining widespread popularity due to their high-performing nature, efficiency, and aesthetic appeal. AHSS is leading the way towards a clean and green future.

NMC’s commitment to AHSS and the future
At National Material Company, we are committed to the processing of advanced high strength steel. We support a variety of AHSS types: Dual Phase, Martensitic, Complex Phase, Trip Steel, and Press Hardened Steel. NMC operates slitting, pickling and cut-to-length steel processing facilities which serve the needs of the steel industry and prominent industrial and consumer product manufacturers.
Steel service center National Material of Mexico (NMM) expanded their facilities in order to meet customer demands for AHSS. NMM invested in their slitting capacity by purchasing the Red Bud AHSS Wide Slitting Line. The Red Bud steel slitter is specifically designed to manufacture and process ultra-high tensile material.
National Material Company’s commitment to the future of steel, the automotive industry, and the planet allows them to continue their legacy as a top steel service center.
About National Material Company L.P. – With more than 3,000 employees from a multinational portfolio of companies, NMLP provides engineered metal products which include aluminum extrusion and stainless steel rolled product companies to supply automotive, aerospace, construction, defense, electrical, and industrial markets. Request a quote online or give us a call (U.S.) 847-806-7200.





